Evidence suggests that prenatal viral infections contribute to dissociative disorder Several weeks after being fired from a job as a Physics teacher he had held for more than 20 years Todd awoke one morning in a state. He suggested it might hold the mechanism for neurodevelopmental changes.

Oxytocin Levels In New Parents New Baby Products New Parents Oxytocin
Several studies have revealed respiratory transmission of viral infection.

. The evidence suggests an increased risk of HIV transmission due to the HIV-positive partner having an STD. Indirect evidence of STDs increasing the infectiousness of HIV exist. Identify the major viral and bacterial RTIs and their sequelae.
Although pregnant women are not more likely to contract the virus infected mothers have an. The Associated Press. Alcohol and smoking are two common teratogens.
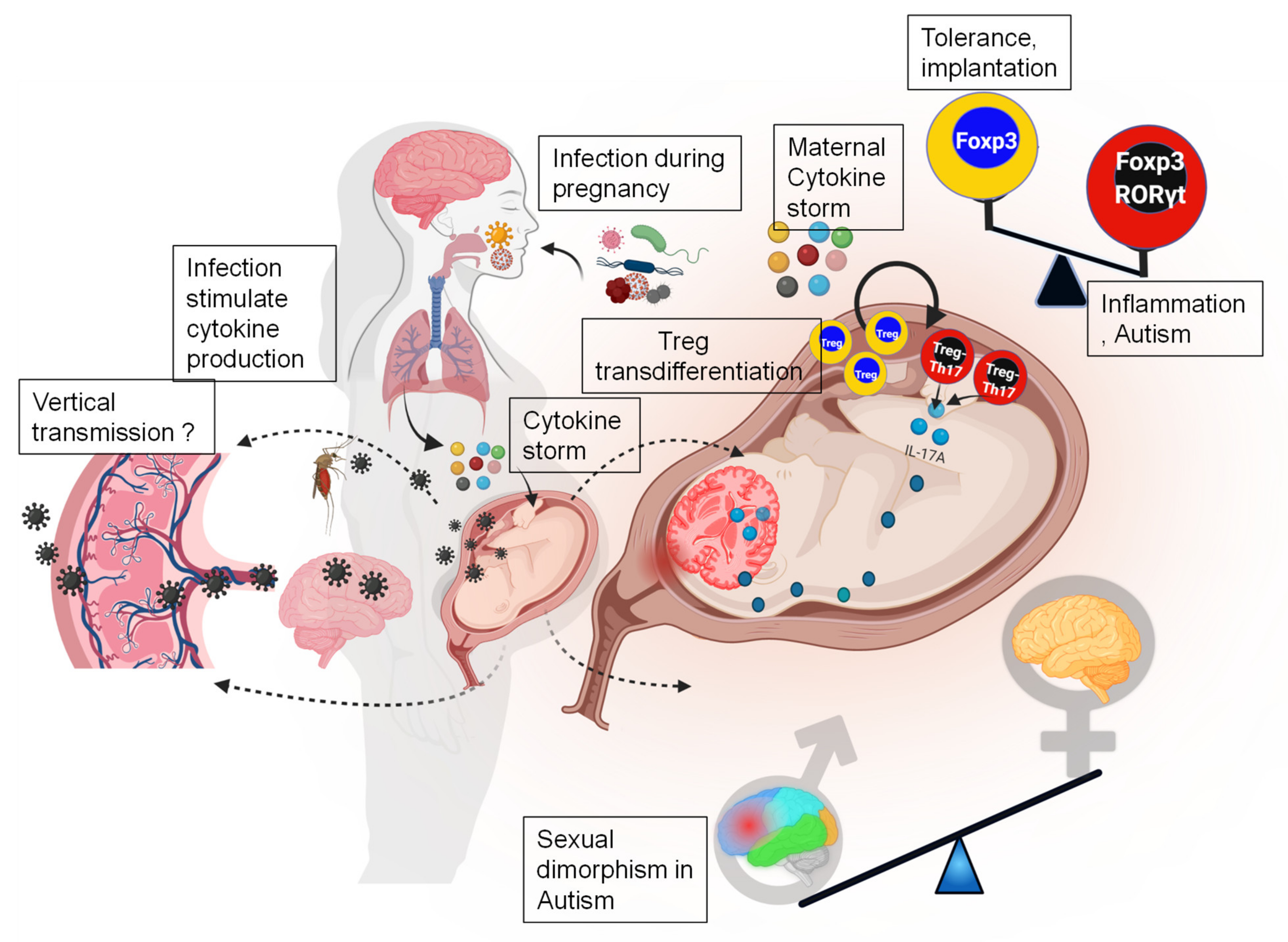
Congenital rubella syndrome is the most convincing environmental cause of autism. The in vitro data presented in this study suggests that viral infection may contribute to the pathophysiology of pregnancies complicated by pre-existing maternal obesity andor GDM. Brown of Columbia University showed that prenatal infections such as rubella influenza and toxoplasmosis are all associated with higher incidence of schizophrenia.
A small study strengthens evidence that a pregnant woman infected with the coronavirus might be able to spread it to her fetus. Researchers from Italy said Thursday that they. These reports emphasized that the oralnasal cavity constituents can be transferred through aerosols andor respiratory.
It is unclear however what the most appropriate estimates are for each population behavior and type of STD given the observational nature of these kinds of studies. Amid the Covid-19 pandemic the risk of viral infection is a cause for both the mother and child. Evidence suggests that prenatal viral infections contribute to A generalized anxiety disorders.
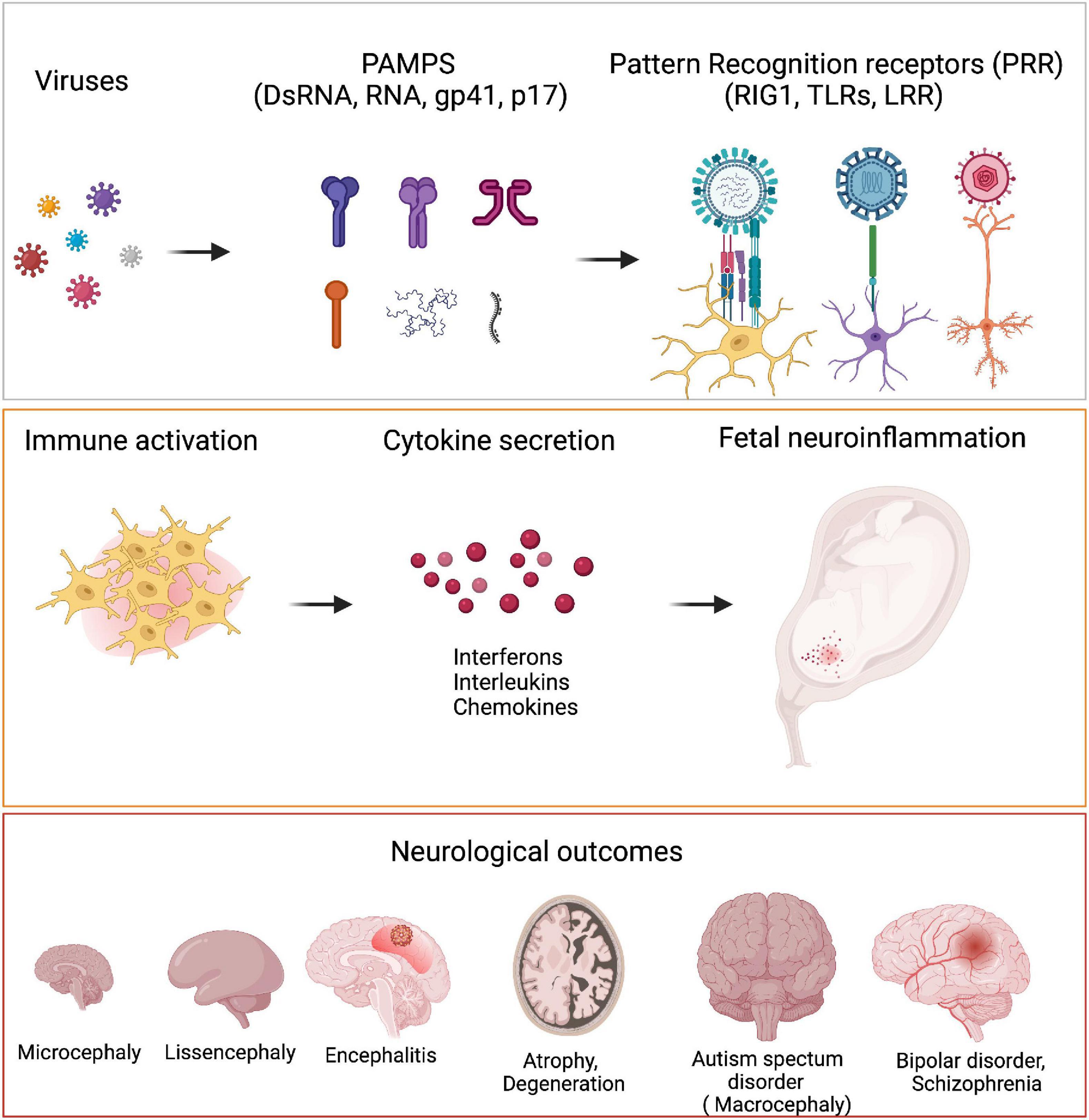
Inflammation is a feature of many of the prenatal conditions Brown has studied. A teratogen is a substance that may lead to birth defects in an embryo or fetus. A study published in the journal Science found that activation in pregnant mice of a particular immune response similar to what may occur with certain viral infections during pregnancy alters the brain structure of the mouse offspring and causes behavioral changes reminiscent of those observed in humans with autism spectrum disorder ASD.
7 Brown found a seven-fold increased risk of schizophrenia when mothers were exposed to influenza in the first trimester of gestation. Certain sexually transmitted infections are known to be associated with preterm birth Baker said namely bacterial infections that can cause irritation in. Mednick et al 1988.
Placentas little helpers Retroviruses which include contemporary viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus HIV and human T-lymphotropic virus HTLV have been infecting vertebrates for over 450 million. Group B Strep can also cause miscarriages stillbirths and preterm deliveries CDC 2014. The in vitro data presented in this study suggests that viral infection may.
During pregnancy exposure to certain chemicals infections and drugs may increase the risk that a person will miscarry or that the embryo or fetus could have a developmental abnormality. SARS-CoV-2 the virus causing the COVID-19 infection can be transmitted from mother to baby before during and after childbirth -- but such occurrences are rare a new study reveals. These data overall illustrate that viral infections during pregnancy can lead to an inflammatory response and structural abnormalities in the placenta.
6 In a 2006 study Alan S. Because a steady stream of research is also beginning to suggest that identifying and treating high-risk individuals may help to ameliorate course and potentially prevent the onset of. Several lines of evidence suggest that the inflammation provoked by a viral infection either before birth or during childhood could trigger the condition in adulthood.
These structural abnormalities may cause significant alterations in oxygen and nutrients delivered to the fetus causing abnormalities in the overall development of the fetus including the brain. It should be noted that the in vitro studies cannot be directly used to infer the same outcomes in the intact subject. A considerable body of literature suggests that prenatal exposure to a viral teratogen PEVT is associated with the etiology of psychotic disorders eg Brown et al 2004.
Epidemiological evidence obtained from other pandemics such as influenza and ebola suggest that pregnant women are more susceptible to serious complications and death from viral infection. Epidemiologic studies suggest that the risk of schizophrenia is increased after prenatal maternal viral infections such as influenza rubella measles and polio as well as infections with. The primary risk factor for neonatal infection transmission is colonization of the mothers genital tract through direct exposure during birth or in fetuses through ascension into the amniotic fluid then into the placenta.
An established marker of inflammation is called C-reactive protein CRP. Intriguingly a mounting body of evidence suggests that the evolution of the placenta had significant assistance from ancient retroviruses. Physiological changes in the anatomical structure of the respiratory system as well as in the immune system during the pregnancy-puerperal period seem to contribute to this greater.
Describe the interaction between reproductive tract infections and family planning child survival safe motherhood and HIV prevention. Prenatal viral infection has been called the principal non-genetic cause of autism. Prenatal exposure to rubella or cytomegalovirus activates the mothers immune response and may greatly increase the risk for autism in mice.
Inflammation a common factor. Understand the general model for the spread of infection and its implications in the control and prevention of RTIs.
Pathogens Free Full Text Pathogenic Infections During Pregnancy And The Consequences For Fetal Brain Development Html
Frontiers Intrauterine Viral Infections Impact Of Inflammation On Fetal Neurodevelopment Neuroscience

Differential Effects Of Early Or Late Exposure To Prenatal Maternal Immune Activation On Mouse Embryonic Neurodevelopment Pnas

0 Comments